To demonstrate the efficienty of the algorithms, let \(f(x)=\sin(x/2)\cos(x/2)\) with \(0\leq x \leq 3\pi\), and this functions can be discretized over an interval \([a,b] = [0,3\pi]\). For example, we can set \(N = 100\) and let \(\Delta x = (3\pi-0)/N\). Thus,
import numpy as np
N = 100
a = 0
b = 3*np.pi
dx = (b - a)/N
x = np.arange(a, b, dx)
Alternatively, we could simply this process by using linspace
x = np.linspace(a, b, N)
Discritizing the function
f= lambda x: np.sin(x/2)*np.cos(x/2)
y = f(x)
To create a nosiy version of this fuction, one can consider adding noise to the data using numpy.random.normal given \(\mu = 0\) and \(\sigma = 0.1\), mean and standard deviation respectively.
mu = 0
sigma = 0.1
noise = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, len(x))
y_noise = y + noise
8.1. Savitzky-Golay Filter#
8.1.1. Savitzky-Golay Filter 1D#
Using Savitzky–Golay filter from scipy package, we can reduce the impact of the generated random noise.
Using a fourth-order polynomial, we get
from scipy import signal
y_filtered = signal.savgol_filter(y_noise, window_length = 23, polyorder = 4)
Let’s plot the data.
from NA_Notes import Reg_Method_Fig1
Reg_Method_Fig1(x, y, y_noise, y_filtered, a, b, f, N)
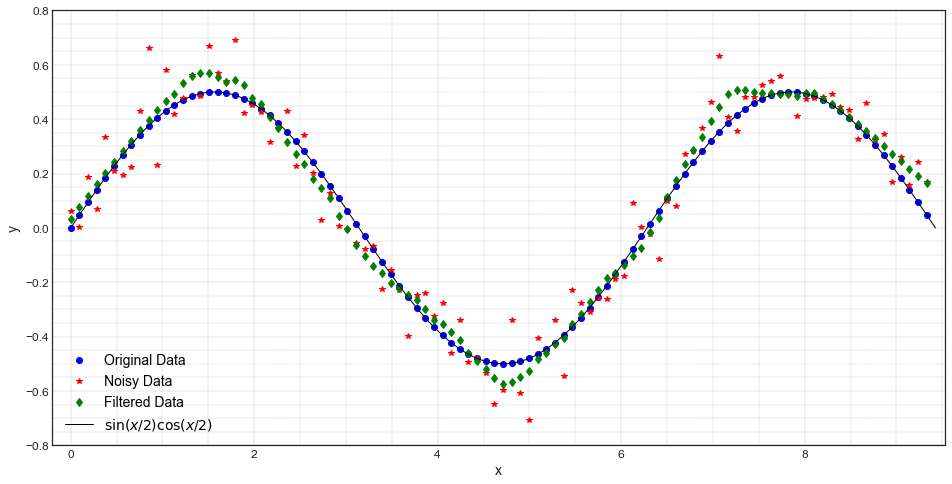
Furthermore, let’s use \(\|.\|_{\infty}\) for mesuring the accuracy.
from IPython.display import display, Latex
from numpy import linalg as LA
display(Latex(r'\|y-y_{noise}\|_{\infty} = %.4f' % LA.norm(np.abs(y-y_filtered), np.inf)))
8.1.2. Savitzky-Golay Filter 2D#
For two dimmentional, we can use the following function from this link
from NA_Notes import sgolay2d, Reg_Method_Fig2
r = 500.
f= lambda x, y: np.cos((x**2)/r + (y**2)/r)
mu = 0
sigma = 0.8
x, y = x, y = np.mgrid[-100:101, -100:101]
z = f(x,y)
z_noise = z+ np.random.normal(mu, sigma, size=x.shape)
z_filtered = sgolay2d(z_noise, window_size = 23, order = 4)
Reg_Method_Fig2(x, y, z, z_noise, z_filtered)
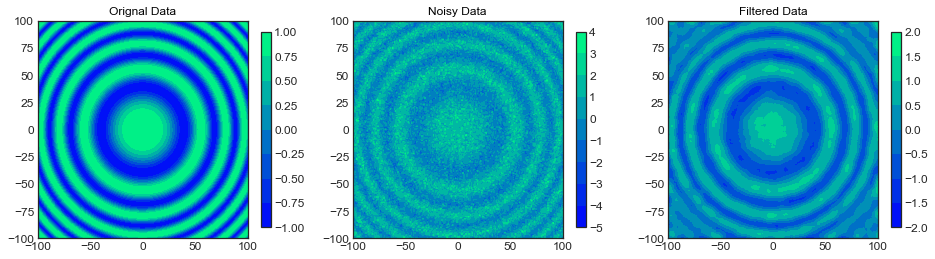
display(Latex(r'\|z-z_{noise}\|_{\infty} = %.4f' % LA.norm(np.abs(z-z_noise), np.inf)))
display(Latex(r'\|z-z_{filtered}\|_{\infty} = %.4f' % LA.norm(np.abs(z-z_filtered), np.inf)))
